What is an Employee Type Agentforce Agent in Salesforce?
Published on: 7/7/2025

Key Concepts of Employee Type Agentforce Agents
Topics
A Topic is a logical grouping inside an Agentforce agent representing a specific capability or intent the agent can understand and handle. It serves as a container for several important elements:
- Classification & Scope
Defines when the Topic is applicable based on user input and restricts what the agent is allowed to do in that context. - Instructions
Text-based guidance that instructs the agent on how to behave when handling the Topic. For example, it might direct the agent to be empathetic, only provide shipping info, or confirm details before making changes. - Actions
These are the concrete tasks the agent can execute within the Topic. Actions can include calling Salesforce flows, Apex classes, APIs, querying databases, or running prompts. Once a user’s request matches the Topic, these actions determine what the agent actually does.
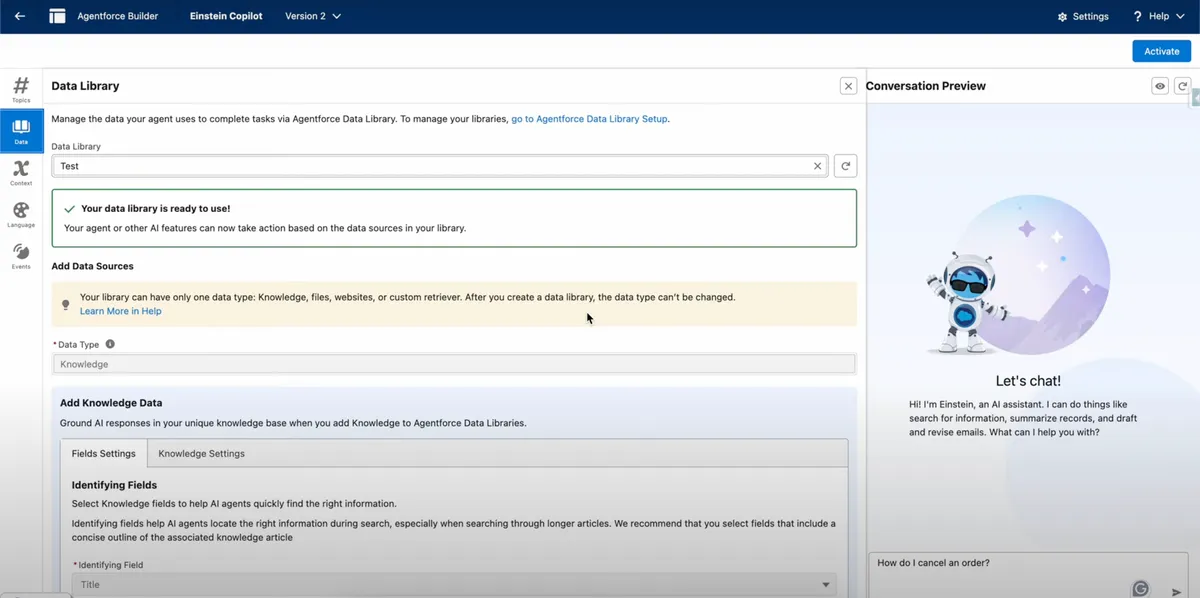
Data Library
The Data Library acts as a centralized repository of data sets, records, and reference information your Agentforce agents access during conversations. It functions like a knowledge base or database, allowing agents to retrieve articles, files, or any other resources needed to provide accurate and dynamic responses.
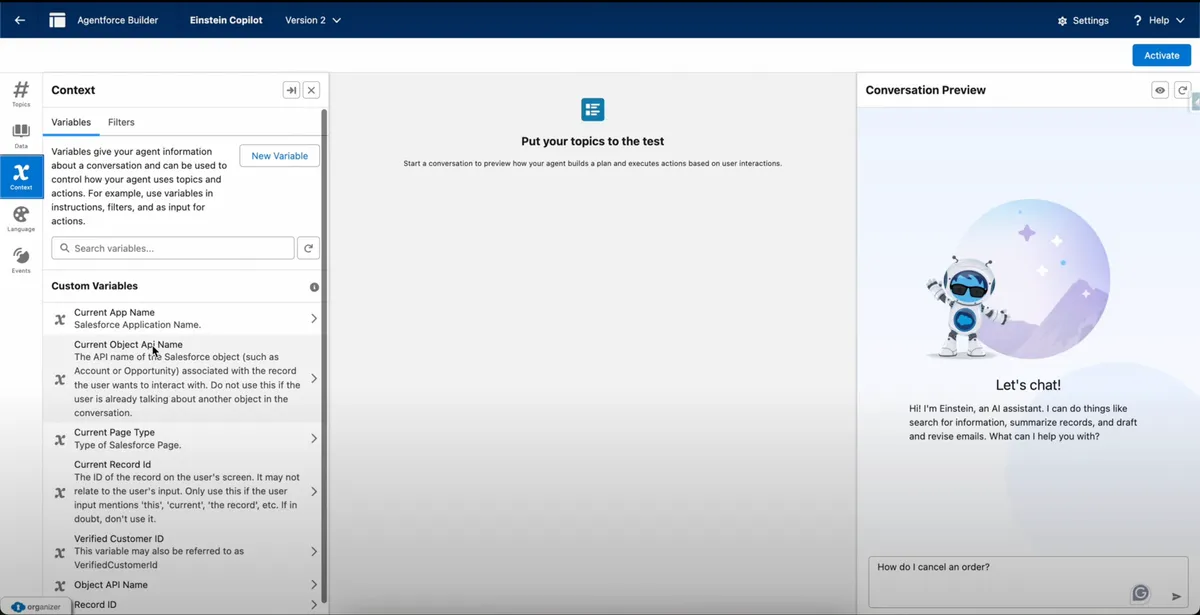
Context and custom Variables
The Context Variables section is used to manage both custom and system-generated variables during conversations. These variables:
- Store session-specific information such as user IDs, case numbers, selections made during the conversation, or any custom data points you define.
- Help maintain continuity in conversations by passing relevant data between different steps or actions.
- Enable dynamic decision-making and personalization based on the current state of the interaction.
Additionally, Filters can be applied to Topics to control when they should be triggered. Filters work by checking if certain context variables (custom or system) are populated or meet specific criteria, ensuring that Topics activate only under the right conditions.
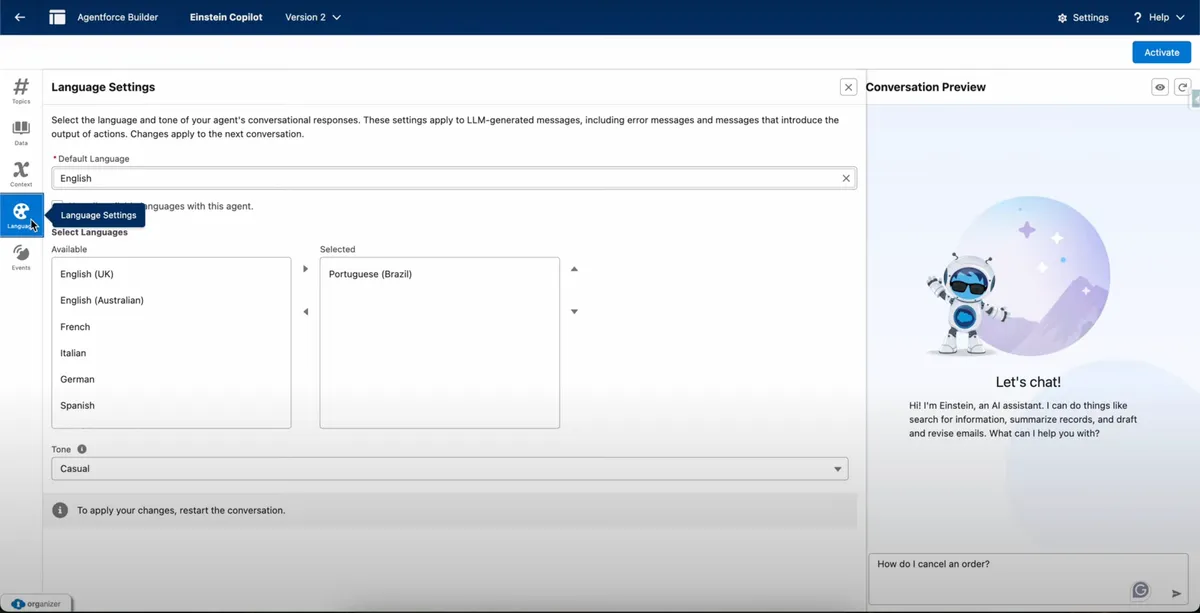
Language Support
Agentforce supports multiple languages, making your agent globally usable. For example:
- If a user interacts in Spanish, French, or any supported language, the agent can understand and respond accordingly.
- This multilingual support makes the Employee Type Agent scalable across different regions and user groups.
Event Logs
The Event Logs section offers a detailed lifecycle view of each session. It helps administrators and developers by:
- Tracking when Topics were triggered.
- Recording which actions were executed.
- Showing how the agent responded at each step.
This is invaluable for debugging and refining your agent, answering questions like:
"Why didn’t this action trigger?" or "Which Topic handled this input?"
Conclusion
An Employee Type Agentforce Agent is a powerful assistant designed to enhance employee productivity by automating routine tasks and providing timely information. By understanding the structure of Topics, the role of the Data Library, Context Variables, Language capabilities, and Event Logs—and by meeting the essential prerequisites—you can build intelligent agents tailored to your organization’s needs.